In almost all cases faster means better. The fastest sportsman becomes a champion, the quickest decision on the stock exchange makes a profit for a trader, finally, only the fastest male reproductive cell has a chance to become a human and bring another life in this world. It isn’t even a philosophic subject for thought – it should be taken as an axiom – in the 21st century our life is speed, and this speed is decisive for lots of processes. In this article, we will focus on the new era in the computing world – “edge computing” that gives the green light to a range of new applications and solves the permanent speed-versus-scale problem.
We develop, and the world around us is evolving too. More devices than a year ago generate more data from more locations. The public cloud still occupies the top place in its computing and storage resources, but getting data there and back takes time and sometimes the speed limits required for this are too long for the work of applications and processes. It especially refers to applications requiring real-time decisions, such as a self-driving truck that needs to “know” when to brake and each second of latency may become catastrophic. Edge computing opens a new door into the world of hundreds of new applications and use cases and could unlock the $40bn incremental market. What are the key drivers of edge computing and which challenges remain crucial? Which apps will be enabled by it and what is the potential for growth? What can we expect from edge computing today and in the near future?
Who Are You? What We Should Know About Edge Computing
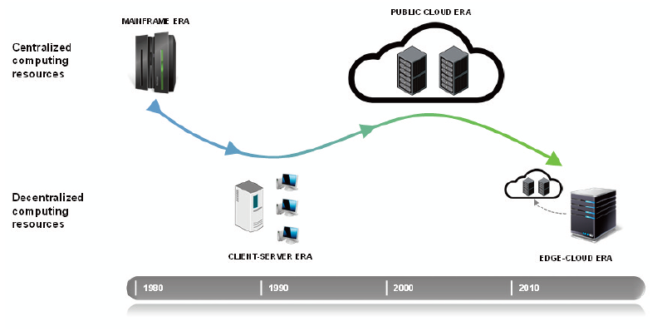
The first question that occurs after hearing all the benefits of edge computing is “What is it?” and “What is the difference from the public cloud?” Edge computing is an entirely new approach to the data storing and computing. However, it isn’t a substitute for the public cloud, it is rather its natural evolution. Instead of competing, they act as complementary models to interact more fluidly with devices at the edge of the network. The main difference between the edge computing and the public cloud is that the data is processed, analyzed, and acted upon at the source of data generation (or very close to it) instead of being sent directly to the public cloud. It allows coping with the central issues of computing – latency and bandwidth. Data is processed immediately, and the lag is as minimal as it’s possible. Sounds good, but how to accomplish this?
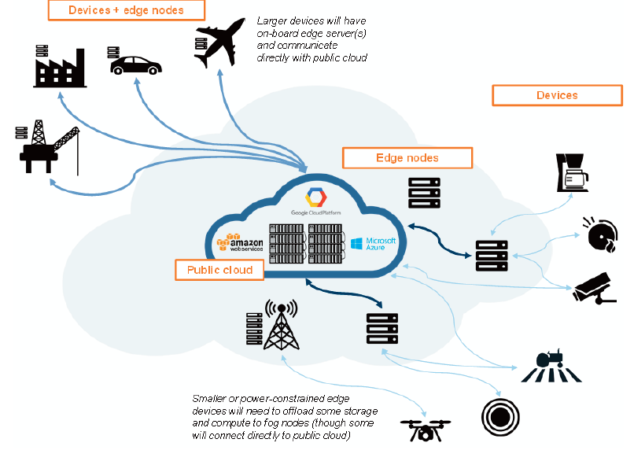
Edge computing adds all the core building blocks of public cloud maximally closer to the origin of the data. It allows insights to be generated and executed in real-time mode. Unlike centrally-located traditional data centers, all edge servers can be placed far from the centralized computing cores, for example, in factories, cars, airplanes, and oil rigs. Thus, bringing pieces and capabilities of the public cloud maximally closer to where data is generated, edge computing significantly minimizes latency and makes it ideal for use cases that require real-time processing. Also, it is a way out where connectivity with the public cloud (networking) is limited.
Apps of the Future or Who Needs Edge Computing?
The unique advantages of the edge servers enable a broad spectrum of use cases that leverage the ability of the edge servers to perform advanced computational tasks at the source of data generation or close to it. It means that use cases as digital oilfields, self-driving trucks, and video analytics are only a small part of all the use cases that will get the ability to revolutionize business processes with the appearance of edge computing. Let’s consider some of the primary potential edge computing use cases for today.
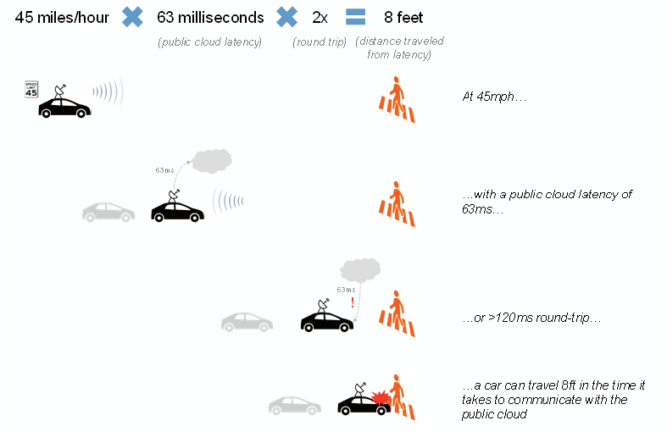
- Self-driving cars and trucks. This use case is impossible without edge computing technologies as the real-time processing via an onboard edge server is critical for the safe operation of the vehicle. Even the smallest latency may become catastrophic for both, the passenger and the general public. Analyzing the data in real-time mode is a task that can only be performed by the edge server. Development of the edge computing may become the primary driver for the autonomous vehicles growth and development. We also believe that edge computing will be a crucial capability required by self-driving cars and truck in the future. The market opportunity for autonomous vehicles is expected to reach $100bn by 2025.
- AR/VR. Augmented and virtual reality use cases require large amounts of processing power. In addition to his, latency is one of the main barriers to AR/VR growth as users are massively sensitive to it. Implementing edge computing technologies can put the augmented and virtual reality on a new level and bring it mass adoption by limiting latency. A common barrier for the AR/VR adoption is nausea that occurs after the prolonged use of VR headset. Technologists have concluded that such “simulation sickness” happens because of the lag of the user’s movement and what is visualized on the screen. Minimizing the latency via edge computing will allow more comfortable and prolonged use of the AR glasses and VR headsets.
- Digital oil rigs. One of the possible use cases for edge computing is oil and gas exploration. Using edge servers for the remote locations of this industry may significantly maximize drills’ output, at the same time, minimizing energy consumption. Analyzing and processing data in real-time is one of the primary difficulties of the industry as the data quickly becomes stale. Using edge computing for the drill data will contribute to making instant decisions about the drill’s next best course of action – whether it should continue the movement, change its direction, or stop. Processing the data with edge services will also significantly lower network and communication expenses that are required to send data back to a data center or a public cloud.
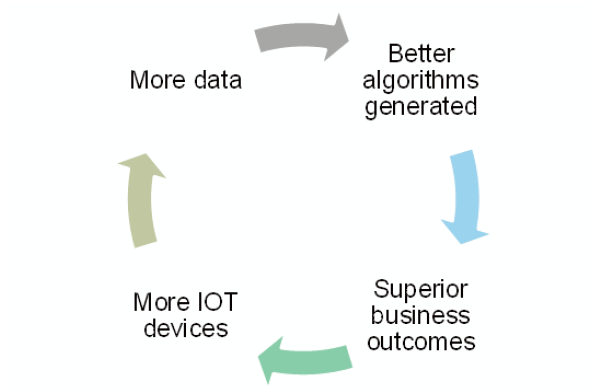
- IoT enterprises. IoT industry is developing rapidly nowadays, and edge services are expected to play a central role in this development. New IoT software platforms where reaction time is the meaning of the existence of the whole system will not be able to work correctly even with the smallest latency. The latency associated with sending the data to the public cloud would eliminate the value of the whole IoT platform. We expect the edge computing systems to play a vital role in the IoT industry by expediting the realization that predictive maintenance is required instead of sending the data to a public cloud.
- Public safety (Amber alerts). Video analytics is another one example when long latency and bandwidth limitations can play a decisive role. For example, searching for a lost child in the city by using video analytics with public cloud limitations will hardly end successfully. In this case, using the edge computing that can analyze the overwhelming amount of the generated data in real-time would be critical for searching. With a wide variety of cameras nowadays in the urban area, including security, traffic, and vehicle-borne options, lots of them can be involved in the searching process. By using edge services, each camera would perform the search independently using computing resources located nearby. In the case when the camera will register the positive match, the data will be immediately uploaded to the cloud by distributing the analytics to all the devices in the edge. After that, tasks can be quickly and efficiently processed.
Who Dictate the Game Rules? Key Drivers of Edge Computing Demand
As in all other developing nowadays industries, in edge computing also there are key drivers that “dictate the rules” of the game and push the development of industry forward. In this case, there are five main drivers influencing edge computing demand.
- Limitations of the device resource. If you compare the edge devices with the full-fledged servers in a data center, of course, forces will be uneven. Edge devices have more limited hardware resources. As a rule, they are limited in the amount of the processing by the onboard hardware. Because of this, such resource as battery/energy consumption is among the most precious ones for edge devices. What to do with the problem? Edge servers located near the edge device will provide it with the constant availability of energy and be able to run the analytics.
- Latency. In lots of use cases where the speed of reaction is critical to the overall system, latency becomes the decisive factor. Even the minimal lag that occurs with a round trip to the cloud via a hub-and-spoke model may not be acceptable. There are many factors influencing the latency, such as network connectivity, other network traffic, a specific region, availability zone, and the data center that the user connects.
- Network connectivity & reliability. Dependence for all data processing and analytic processes on the public cloud is not suitable for many use cases. Low or intermittent network connectivity caused by physical obstructions as hills, building, and forests or bad weather may bring the catastrophic results for use cases like a connected vehicle.
- Bandwidth & storage. With the advent of the public cloud, the speed of data processing has significantly exceeded network bandwidth. However, with the overwhelming amount of data generated by various devices every second nowadays, bandwidth and storage become impossible for public cloud capabilities and even 5G bandwidth is inadequate to upload the vast quantities of data generated by IoT devices.
- Security & privacy. Processing the data at the edge instead of uploading to the public cloud bring excellent results for security and confidentiality overcoming the problem of inherent risks in transmission. Regulatory issues including data residency could also be addressed by leaving all the data at the source of generation or near it.
Conclusions and Highlights
Does edge computing have a chance to become a new era in the era of processing and analyzing capabilities? When will there be the peak of apps of the future development? These questions and lots of other ones require answers. So, what do we have for today?
- Edge computing has all the opportunities to become a key enabler for lots of new apps
- Putting computing and storage devices closer to the source of data generation significantly increase the speed of the signal
- IoT, digital oil rids, self-driving vehicles and lots of other use cases will get a green light with the edge computing development and growth
- The speed-versus-scale problem of modern computing can be solved with edge services
Edge computing has all the chances to open new doors in the world of technologies, becoming the key driver for the development of applications requiring real-time decision-making. Speed without limits, security & privacy, minimal latency, and high reliability – all this characterises edge services. Even being at the early stage of development, edge computing promises impressive results for the existing and new applications.
Recent Comments